Human Residual Host Cell DNA Quantification
A residual host cell DNA that quantifies only the human DNA, not the viral DNA
The Direct Human Residual Host Cell DNA Quantitation Assays are designed to capture human DNA through DNA hybridization, and directly measure residual human host cell DNA.
Human cell lines such as HEK293T and 293 cells are commonly used to produce adenovirus and lentivirus particles for gene and cell therapy. The residual host cell DNA in this manufacturing process can either come from within the virus capsids or in the unpurified lysates. Quantification of these total residual host cell DNA can be done through a sample pre-treatment process followed by the direct DNA assays using the Direct Human Residual Host Cell DNA Quantitation Assays. The assays can provide a detection limit of 0.09 ng/ml DNA (1.8 pg in 20 ul assay) with a linear range between 0.09 ng/ml and 25 ng/ml using Luminex MAGPIX or similar results with a luminometer.
VznHealth™ Direct Human Residual Host Cell DNA Assay
Signal detection by a luminometer.
Catalog Number: DC-08-0596R
Pack Size: 96 Reactions.
Research Service is also available.
QuantiDNA™ Direct Human Residual Host Cell DNA Assay
Signal detection by Luminex MAGPIX
Catalog Number : DC-08-0396R
Pack Size: 96 Reactions.
Research Service is also available.
Input DNA
10 µl lysate with DNA within the dynamic range
GET A QUOTE NOW
Advantages of the Direct Human Residual Host Cell DNA Quantitation Assay
NO DNA EXTRACTION NEEDED
The Assays do not extract DNA and directly quantitate the residual DNA from the cell lysate
IDENTIFY HOST CELL RESIDUAL DNA
The Assays specifically quantify the DNA contamination from human host cells, rather than plasmid or virus DNA.

NON-SPECIFIC DNA SEQUENCE
The Assays use non-specific DNA sequence methods. It helps identify and quantify different sequences of contaminant DNA
Why is Residual Host Cell DNA Quantification Necessary?
In the modern pharmaceutical industry, it is common to make protein drugs or gene therapy virus particles such as adenoviruses or lentiviruses in host cells. Biopharmaceutical impurities such as residual host proteins and DNAs from the manufacturing process may bring toxicity and safety issues to patients. WHO and FDA have clear guidelines to control the amount of these impurities in the final drug products to reduce their harm to human health.
Therefore, different categories of pharmaceutical impurities must be quantified to meet the regulatory requirements and ensure drug safety, stability and efficacy.

Residual Host Cell DNA Quantification Methods
Multiple DNA quantification methods are developed for the determination of residual host cell DNA, including non-specific DNA sequence methods and specific DNA sequence methods. The following four types of methods have been developed and validated for this application:
DNA-Binding Dye
Immunoassay
DNA Hybridization
qPCR Assay
All these methods have their advantages and disadvantages and the users will need to carefully select them depending on:
Specific detection needs on process impurity or product impurity
Assay limitations on assay sensitivity and host cell specificity
Drawbacks on the Current Methods
Methods such as DNA-binding dye and qPCR assays need DNA extraction before quantitation to remove any interferences from the matrix such as high protein or high salt concentration. Although automated DNA extraction is available now in the industry and the quantitation bias resulted from DNA extraction can be calibrated, these steps add more work and higher cost to the quantitation.
The Human Residual Host Cell DNA Quantification Assay is Powered by SuperbDNA™ Technology
One of the hybridization methods is the use of SuperbDNA™ technology, which modifies the bDNA technology to quantify DNA. Different from traditional DNA hybridization methods, the SuperbDNA™ technology amplifies chemical signals through a series of DNA hybridizations and therefore assay sensitivity has been drastically increased without DNA or RNA target amplification. Unlike DNA-binding dye or qPCR assays, DNA quantification methods based on SuperbDNA technology directly measure the concentration of the samples without DNA extraction, reducing errors or mitigating the calibration needs during the DNA extraction step.
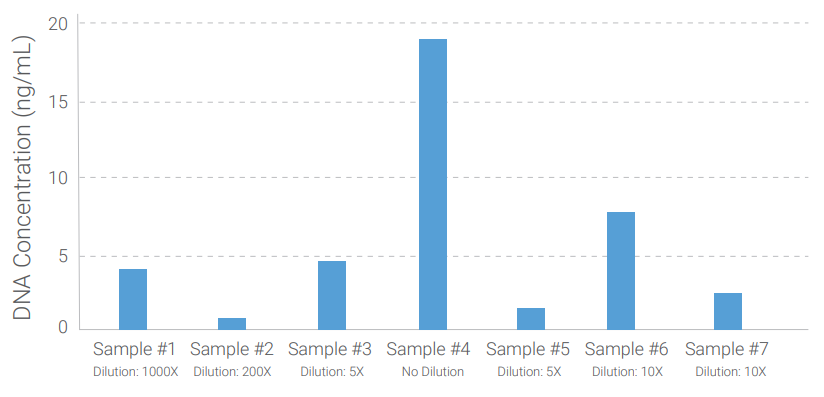
Detection of Residual DNA from HEK293 Cells for Lentivirus Particle Production
To determine the human residual host cell DNA, we tested samples from HEK293 Cells for Lentivirus particle production.
The figure on the right shows samples with different amounts of residual DNA detected by QuantiDNA™ Direct Human Residual Host Cell DNA Assay.
Figure: Lentivirus particle production sample quantitation for residual HEK293 DNA
To determine the human residual host cell DNA, we tested samples from HEK293 Cells for Lentivirus particle production.
The figure on the right shows samples with different amounts of residual DNA detected by QuantiDNA™ Direct Human Residual Host Cell DNA Assay.
Figure: Lentivirus particle production sample quantitation for residual HEK293 DNA
The Direct Human Residual Host Cell DNA Quantification Assays Are Specific for Human DNA
The specificity of both assays was evaluated by testing bacterial genomic DNA from ZymoBIOMICS™ Microbial Community DNA Standard which is a mixture of genomic DNA isolated from pure cultures of eight bacterial and two fungal strains. No significant difference was observed in the signal between blank control and bacterial DNA at 500 ng/mL tested with 3 lots of kits, indicating no false-positive results for bacterial DNA samples.
The table on the right shows the testing result using the QuantiDNA™ Direct Human Residual Host Cell DNA Assay.
Table: Fluorescence signal of blank control vs bacterial DNA. n/a: not tested
| Sample # | Sample | MFI-1 | MFI-2 | MFI-3 | MFI-4 | Avg | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lot-1 kit | Bacterial gDNA (500 ng/mL) | 7 | 7 | 7 | n/a | 7.0 | 0.0 |
| Blank Control | 6 | 7 | 7 | n/a | 6.7 | 0.6 | |
| Lot-2 kit | Bacterial gDNA (500 ng/mL) | 8 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 7.0 | 0.8 |
| Blank Control | 7 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 8.3 | 1.3 | |
| Lot-3 kit | Bacterial gDNA (500 ng/mL) | 6 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 6.3 | 0.5 |
| Blank Control | 6 | 7 | 11 | 9 | 8.3 | 2.2 | |
