Cancer Progression and Therapy Response Monitoring
RadTox™ measures the cell-free (cfDNA) levels at different stages of cancer management for various cancer types.
CE/IVD Marked Product
Research Use Product
CLIA-Certified Lab Service
Research Service
Early Detection
Diagnosis
Therapy Selection
Therapy Monitoring
Introducing RadTox™ Test
RadTox™ Test measures the changes over the whole treatment process, offering essential insights into the patient’s cancer progression and therapy response prior to the availability of imaging tools, which might only become accessible three months post-therapy, potentially beyond an optimal decision-making timeframe.
Simple blood test: only 2 tubes of blood needed
Treatments that could potentially benefit from RadTox include surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, immunotherapy, combination therapy, and more
Predict cancer progression and treatment response to anticancer therapy earlier than current standard-of-care
Based on DiaCarta's proprietary QuantiDNA™ Direct cfDNA Test technology
Monitoring Your Patient Therapy without Changing the Standard Care
The lack of a reliable biomarker in cancer therapy monitoring makes standard care heavily rely on imaging. We have developed a commentary liquid biopsy test, the RadTox test, to monitor the therapy responses, such as response to radiation therapy or chemotherapy. Watch this video and see how we have used the test to monitor patients of different cancer types for disease progression or stable disease conditions.
Why do we measure cfDNA?
Personalized medicine has come into our life with technology advancement and molecular biomarker development. Disease monitoring throughout the cancer management journey using liquid biopsy holds a great future for personalized medicine. Traditional biomarkers, including carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), are often less sensitive to cancer patient prognosis and therapy efficacy monitoring.
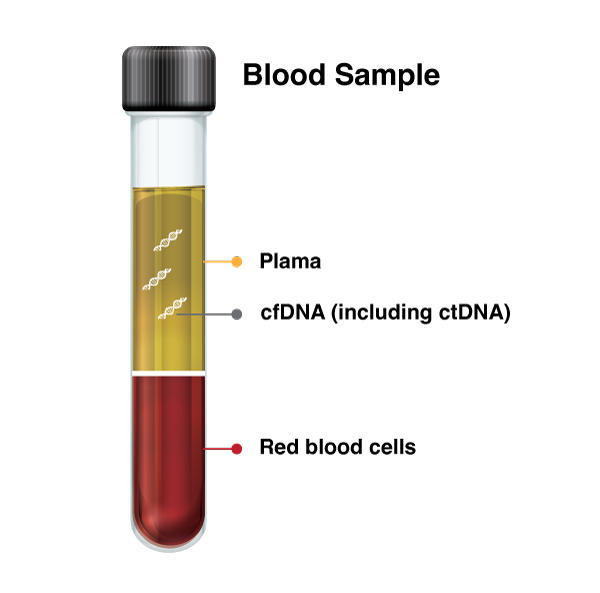
Circulating Tumor DNA (ctDNA)
ctDNA is part of cfDNA, accounting for 0.01 to 10% of the total cfDNA depending on different stages of disease and therapy.
CtDNA blood levels indicate cancer progression and therapy effectiveness (e.g., MRD)
Measuring the amount of ctDNA in the blood has shown great potential in helping doctors keep track of cancer progression and therapy responses, e.g., MRD.
Molecular Residual Disease (MRD) refers to tiny amounts of cancer cells that may be left in the body after treatment, which can be hard to detect but could cause a person’s cancer to come back in the future.
MRD monitors residual cancer cell and tumor recurrence
MRD can be a personalized tool for monitoring residual cancer cells and the return of the tumor due to clone evolution (recurrence).
Molecular Residual Disease (MRD) refers to tiny amounts of cancer cells that may be left in the body after treatment, which can be hard to detect but could cause a person’s cancer to come back in the future.
Bottleneck: prior cancer mutation signature information required
Tissue-informed ctDNA MRD often requires prior cancer mutation signature information. It is not always easy to implement clinically due to complicated procedures or a lack of tissue specimens
Bottleneck: MRD is more costly and more time-consuming
The MRD monitoring will need to be optimized if personalized MRD is desired. This means more time is needed to get the personalized MRD panel ready
Cell-Free DNA (cfDNA)
cfDNA is tiny pieces of DNA that float around in your blood, which can come from any type of cell in your body, not just cancer cells, and can help doctors learn more about your health.
cfDNA quantification is proportionally correlated with ctDNA quantification
Clinical research studies have indicated that cfDNA quantification is proportionally correlated with ctDNA quantification.
Source: Hu et al. Post surgery circulating free tumor DNA is a predictive biomarker for relapse of lung cancer. Cancer Medicine 2017; 6(5):962–974.
No need for prior cancer mutation signature information
Direct quantification of cfDNA does not need prior knowledge of the ctDNA mutation signature of individuals and it can be applied to all patients of various cancer types.
cfDNA is easy to be measured using the RadTox™ Test
No DNA extraction and only 10 ul plasma are sufficient for one assay.
Measuring cfDNA is more clinically feasible
cfDNA measurement is more clinically practical as it may get near real-time data if the facility is in the lab next door.
Therefore, we developed the RadTox™ Test for cancer progression and therapy responses monitoring based on cfDNA quantification.
Determining the time point for using the RadTox™ Test in cancer management
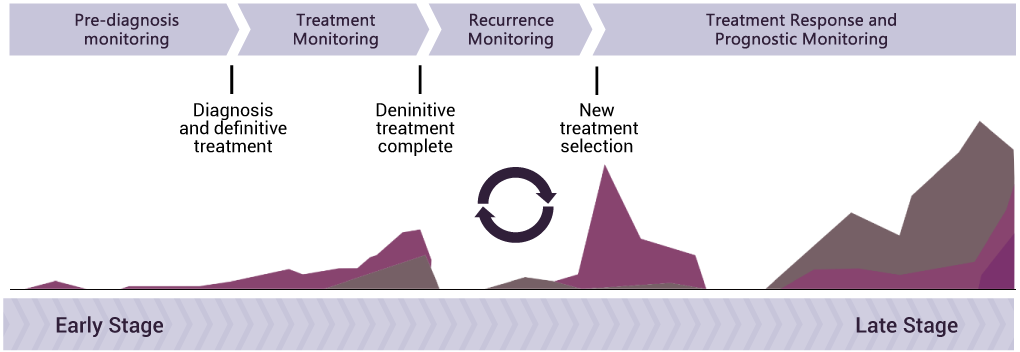
RadTox™ test is used in monitoring the whole cancer management process starting from the point of diagnosis. Collecting blood samples at various time points of cancer management equips physicians to make well-informed decisions with comprehensive patient evaluation.
Before treatment
During treatment
After treatment
At follow-up appointments
Before imaging
What information does RadTox™ result provide?
cfDNA level before treatment, i.e., the baseline level, is often correlated with prognosis
Source
Henriksen et al. The effect of surgical trauma on circulating free DNA levels in cancer patients—implications for studies of circulating tumor DNA. Mol Oncol. 2020 Aug; 14(8): 1670–1679.
During the treatment, the cfDNA level will increase immediately due to the fact that the therapy kills cells
Sources
Source 1: Kwee et al. Measurement of circulating cell-free DNA in relation to 18F-fluorocholine PET/CT imaging in chemotherapy-treated advanced prostate cancer. Clin Transl Sci 2012 Feb;5(1):65-70.
Source 2: Zhong et al. Plasma cfDNA as a Potential Biomarker to Evaluate the Efficacy of Chemotherapy in Gastric Cancer. Cancer Management and Research 2020:12 Pages 3099—3106
Three weeks to one month after therapy, the cfDNA level shall come down if the therapy is effective but may remain at a similar level or even increase compared to the pre-treatment if the treatment is ineffective
Sources
Source 1: Zhou et al. Kinetics of plasma cfDNA predicts clinical response in non small cell lung cancer patients. Scientifc Reports | (2021) 11:7633.
Source 2: Lockney NA, et al. Circulating Cell-Free DNA Correlates with Body Integral Dose and Radiation Modality in Prostate Cancer. Int J Part Ther. 2020 Sep 15;7(2):21-30. doi: 10.14338/IJPT-20-00033.1
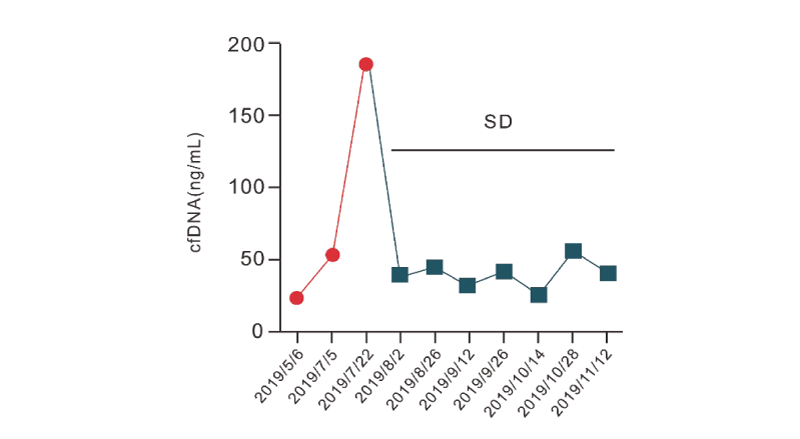
The rectal cancer patient went through chemotherapy between May and July 2019. RaxTox™ monitoring started in May. The RadTox™ score reached its highest in late July and came down in early August. The RadTox score stayed stable till the last monitoring point in November. The patient remains in stable condition.
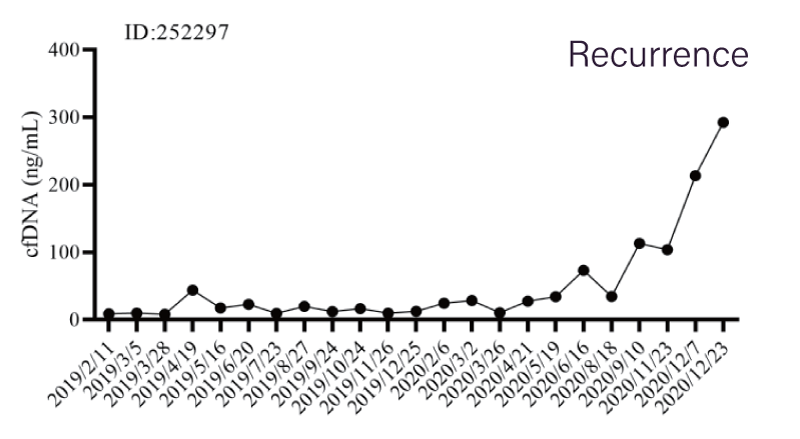
The esophageal cancer patient stabilized after treatment. RadTox score stayed low during the period of February to August 2020. Then the RadTox™ score started to increase when the cancer recurrence occurred.
The DiaCarta offerings
PRODUCT
RadTox™ is a CE/IVD marked product for countries with CE/IVD compliance. It could also be used as a research product in the United States.
- Pack size: 96 reaction
- RadTox™ utilized a straightforward methodology with no sample preparation or PCR
SERVICE
RadTox™ is available at DiaCarta CLIA as a Lab-Developed-Test (LDT).
Simple blood test: only 2 tubes of blood needed
Fast turnaround time: report ready in 5 business days upon sample receipt
Disclaimer: RadToxTM Test is performed at the DiaCarta Clinical Laboratory as a Laboratory Developed Test (LDT). It was developed by DiaCarta with performance characteristics determined by DiaCarta, based on clinical studies on radiation toxicity assessment on prostate cancer patients. The test is not cleared or approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). This test has been validated at the DiaCarta Clinical Laboratory pursuant to CLIA regulations and can be used for clinical purposes. The test results may be used along with other therapies and cancer types, but the result interpretation has not been validated and should be used with caution by medical professionals. This test has not been investigated or validated for use in inhaled radiation. DiaCarta is not responsible for the clinical decisions made based on this test. The DiaCarta Clinical Laboratory is regulated under CLIA regulations and is qualified to perform high-complexity testing.
