Single Gene Mutation Detection Tests
Improved Sensitivity for Single Gene Mutation Detection. Products are available for KRAS, NRAS, EGFR, BRAF, JAK2, and PIK3CA.
CE/IVD Marked Product
Research Use Product
Research Service
Early Detection/Screening
Diagnosis
Therapy Selection
Therapy Monitoring
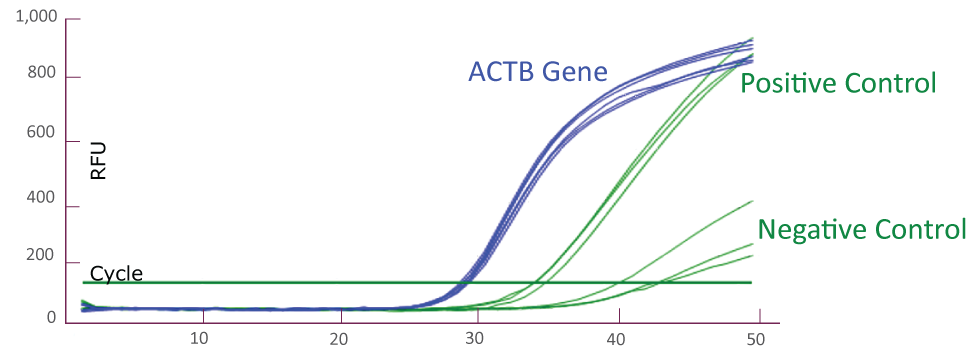
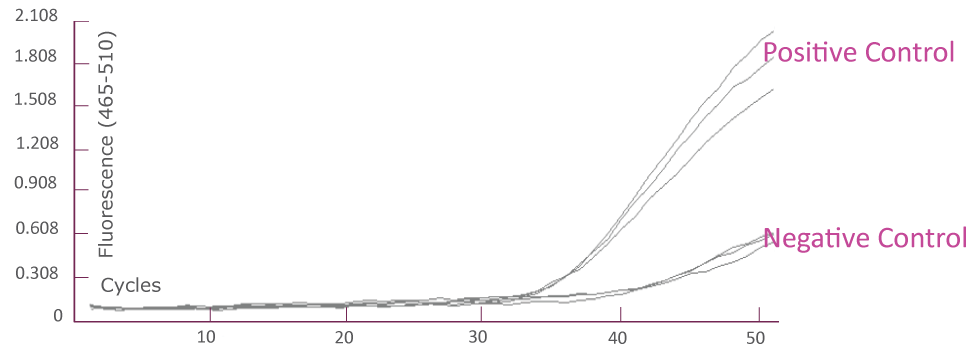
QClamp® Gene Mutation Detection Tests are highly sensitive qPCR-based assays for tissue biopsy (FFPE) and liquid biopsy (ctDNA) applications. QClamp® assays reliably detect 0.1% to 0.5% mutant DNA out of wild-type DNA for targeted mutations, providing lower detection limit compared to similar assays available in the market due to robust enrichment of mutant sequences while suppressing amplification of wild-type sequences.
QClamp® assays provide a rapid, reproducible and affordable solution that employs a simple workflow and utilizes PCR machines that are commonly used in research and clinical labs. The tests can be performed on standard real-time qPCR instruments such as ABI QuantStudio 5, Roche LightCycler® 480 and Bio-Rad CFX384.
QClamp® Gene Mutation Detection Test Offerings
QClamp® KRAS Mutation Detection Test
Detects codons 12, 13, 59, 61, 117 and 146 for FFPE and plasma samples.
QClamp® NRAS Mutation Detection Test
Detects codons 12, 13, 59, 61, 117 and 146 for FFPE and plasma samples.
QClamp® EGFR Mutation Detection Test
Detects codons 719, 861, Ex19del, Ex20insASV and S768I, T790M and L858R mutations for FFPE and plasma samples.
QClamp® BRAF Mutation Detection Test
Detects codon 600 for FFPE and plasma samples.
QClamp® JAK2 Mutation Detection Test
Detects codon 617 for plasma samples.
QClamp® PIK3CA Mutation Detection Test
Detects codons 542, 545 and 1047 for FFPE and plasma samples.
Advantages of QClamp® Gene Mutation Detection Test

ULTRA-SENSITIVE
Reliably detects 0.1% to 0.5% VAF mutant DNA out of wild-type DNA for targeted mutations

SAMPLE READY
Suitable for plasma and FFPE samples

LOW INPUT DNA
Minimum 5ng input DNA per reaction. Less than 2 tubes of blood (10mL each) needed for cfDNA
COMPREHENSIVE COVERAGE
Covers all relevant somatic mutations in KRAS, NRAS, EGFR, BRAF, JAK2 and PIK3CA oncogenes
FAST RESULTS
Less than 4 hours of assay run time

GREAT VERSATILITY
Validated on the most common qPCR machines with minimized variability
Gene Mutation Detection and Cancer
Accurate diagnosis of cancer mutations is critical for determining optimal therapy and to save or extend cancer patients’ lives. With the identification of different types of biomarkers, including genetic biomarkers, cancer patients can now get much more detailed genetic profiling rather than just understanding generic information such as cancer types. With such detailed genetic profile information, a targeted therapy regimen can then be applied using the personalized medicine approach.
A great example is the targeted therapy for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) using companion diagnostics to identify EGFR mutations at different stages of the therapy, and applying different tyrosine inhibitor drugs based on the specific EGFR mutation present.
Challenges for Detecting Cancer Mutations
It is challenging to be able to detect the mutations residing in a small population of tumor cells within a large number of normal cells.
The first challenge is to get the tumor tissue that contains more tumor cells. Pathologists can use micro-dissection to increase the chance of getting more tumor cells in the testing samples
The next challenge is the testing method. Multiple testing methods have been used in the labs to detect cancer gene mutations, but low sensitivity has been a major concern in identifying mutations in limited tumor samples. An optimal method is the one that not only saves time and cost, but also has sufficient analytical sensitivity
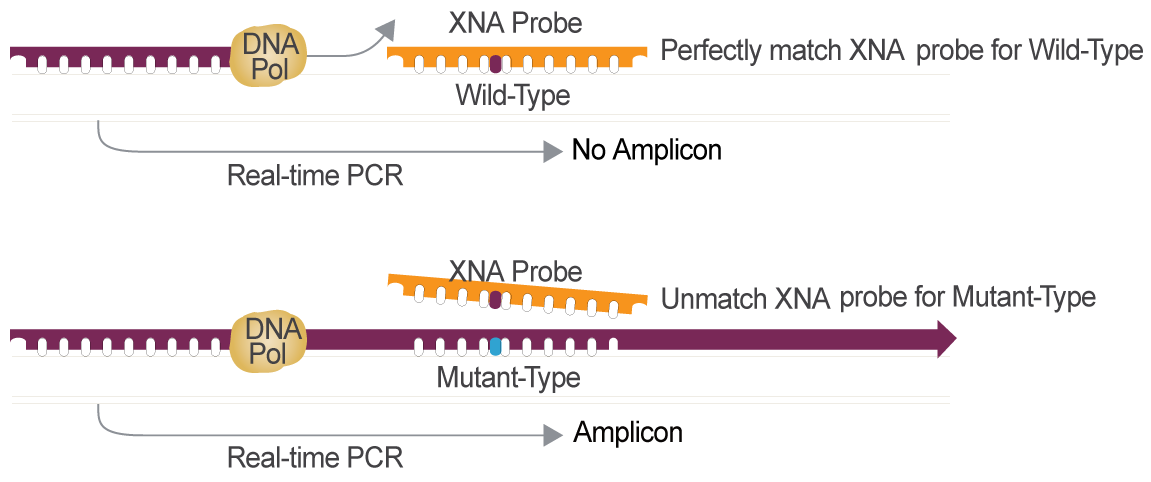
Cancer Gene Mutation Detection Powered by XNA Technology
XNA is the Optimal Choice for Cancer Gene Mutation Detection Compared to other Technologies
XNA,

Sanger Sequencing
Advantage: accurate result and is, therefore, the gold standard
Disadvantage: low sensitivity (20% to 25% VAF)

Pyrosequencing Assays
Advantage: better sensitivity and throughput than Sanger sequencing; the early form of NGS assays
Disadvantage: low sensitivity (5% to 8% VAF)

NGS Sequencing
Advantage: high-throughput and good sensitivity (1% to 5% VAF, or even better)
Disadvantage: costly and time-consuming (7 to 10 days)

Digital Droplet PCR (ddPCR)
Advantage: high sensitivity (claimed to be 0.001% VAF)
Disadvantage: much less sensitivity observed in testing than claimed and suffers from false-positive results

qPCR Analysis
Advantage: Sensitivity can reach 1% VAF for some targets. Rapid with minimal hands-on work.
Disadvantage: Multiple methods available for qPCR and a lot of variations in sensitivity. Some of them are only 10% VAF
Supporting Data
Below 0.1% Detection Sensitivity of Mutant DNA
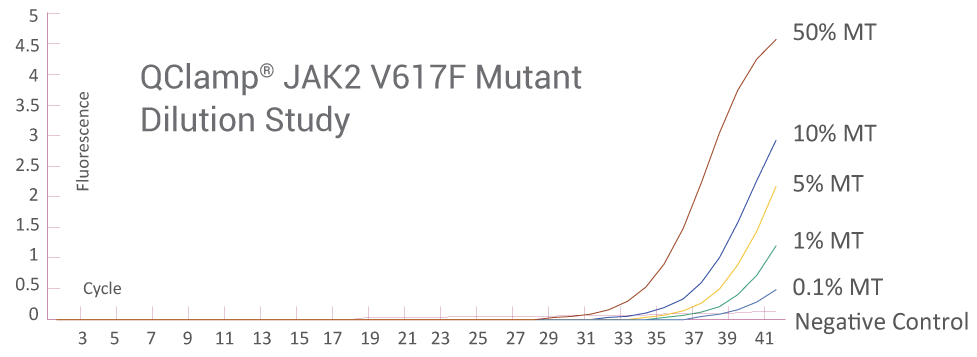

Amplification Plot from ABI QuantStudio 5 (JAK2)

Amplification Plot from Bio-Rad CFX384 (JAK2)

Amplification Plot from Roche LightCycler® 480 (JAK2)

Streamlined Workflow for QClamp® Gene Mutation Detection Tests

Step 1: DNA Isolation & Quantification
Extract DNA from FFPE or plasma using a commercial DNA extraction kit and measure the concentration using fluorometric analysis

Step 2: set up qpcr
Mix the assay reagents, load into PCR plate, add controls and extracted DNA ~ 30-60 minutes
Step 3: Amplification parameters
Enter amplification parameters on
qPCR instrument, load PCR plate
and start the run ~ 2.5 hours
Step 4: Data analysis
Determine the presence or absence
of mutations according to the Cq
value cutoffs ~ 15 minutes
QClamp® Assays Limit of Detection (LoD)
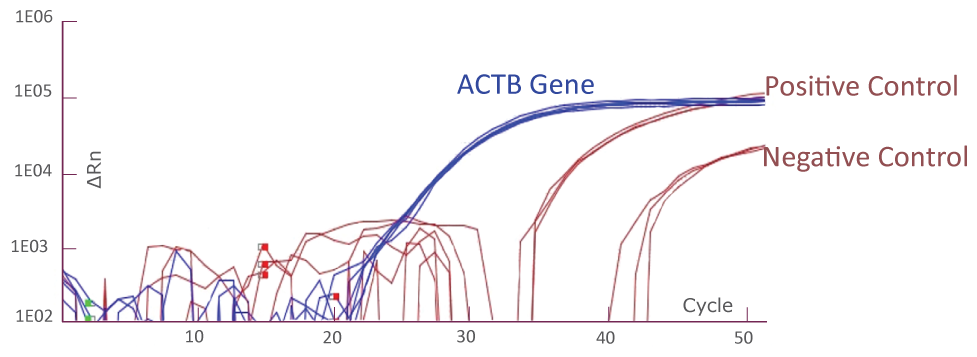
The LoD for the qPCR assay is determined by running the QClamp® assay using a serial dilution of mutant DNA in wild-type background at different total DNA inputs and several mutation frequencies for each target. To determine if a sample is positive (contains mutation) or negative (does not contain mutation) for a particular target sequence, the ΔCq of the sample at this target sequence and the validated standard ΔCq for this target sequence for a positive and negative control will need to be compared.
Cq difference (ΔCq) = Sample Assay Cq – Internal Control Assay (beta-actin) Cq
If further sequencing is required, the qPCR reactions can be sequenced directly by Sanger sequencing using target-specific primers.
QClamp® Gene Mutation Detection Test Product Specifications
Intended Use
For in vitro diagnostic use (CE/IVD) or for research use
Sample Type
FFPE and Plasma
Input DNA
5-10ng/Reaction
Pack Size
30 Samples
Instruments Validated
Roche LightCycler® 480, Bio-Rad CFX384 and ABI QuantStudio 5
Detection Chemistry
TaqMan
Turnaround Time
Less Than 4 hours
Stability
Stable for 12 Months at -25°C to -15°C
Utilizing QClamp® on Clinical Sample Mutation Detection
CLINICAL SAMPLES
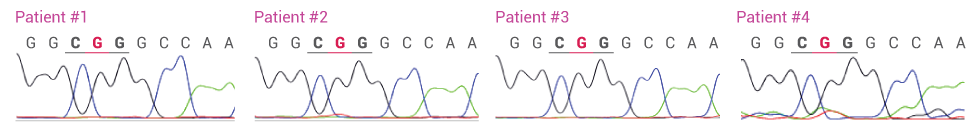
NSCLC Patients Plasma Samples
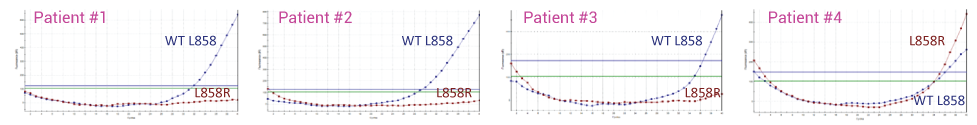
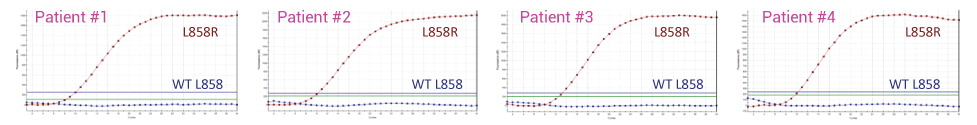
Detecting L858R in Plasma from four NSCLC Patients with and without XNA. In the absence of XNA only wild-type sequence is detected. In the presence of XNA, only the mutant DNA is detected.
Without XNA Technology – Mainly Wild-Type (WT) L858 Detected

With XNA Technology – Wild-Type Blocked, only L858R Mutant Detected

L858R Detected by Sanger Sequencing after XNA Blocking (WT = CTG; L858R = CGG)

CLINICAL SAMPLES
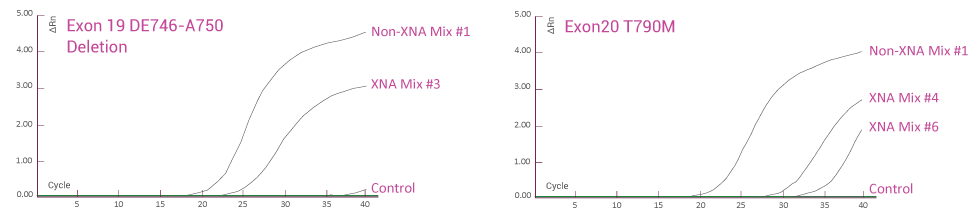
Human Tumor FFPE Samples
Human tumor FFPE samples for EGFR gene mutation detection. EGFR mutations (Exon 19 deletion and T790M) in human tumor FFPE samples are detected using QClamp® EGFR detection kit. Abundant wild-type DNA is detected at early qPCR cycles when no XNA is present. With XNA, only mutant DNA is detected at late qPCR cycles and wild-type DNA amplification is blocked.